9. Appendix: Course Software
You can choose either or both of the following options.
9.1. Cloud-based development environment
This option is recommended if you have any problems with your local setup or if you prefer a basic cloud-based setup.
9.1.1. Pros
consistent, cloud-based environment
out-of-the-box integration with GitHub
9.1.2. Cons
requires good network connection
might lack some code completion features
free plan might be underresourced (CPUs, RAM, disk space, etc.)
lack of integration with external GUI-based tools
9.1.3. GitHub Codespaces (recommended)
GitHub Codespaces is a cloud-based, containerized development environment based on Visual Studio Code running on Ubuntu LTS and closely integrated with GitHub.
To use Codespaces,
log into using your GitHub account and navigate to the desired repository
look for the blue “code” button and open the drop-down menu
select the Codespaces tab
create a new Codespace for this repo or open an existing one already linked to this repo
For more information, please refer to this reference.
9.2. Locally installed development environment
This option will give you an advanced development environment with code completion, type info, etc.
9.2.1. Pros
provides powerful capabilities, including code completion and refactoring
does not require network connection once installed
9.2.2. Cons
might be slow on older machines
need to maintain on each machine you use, but can use settings sync to keep settings and extensions consistent
it can be challenging to match the versions of the various packages
GitHub account access might be tedious to configure
possible difficulty managing coexisting Java versions
9.2.3. Required packages
Git distributed version control system (usually preinstalled on Mac OS and Linux)
recommended installation option on Windows: Use Git and optional Unix tools from the Windows Command Prompt
optional on any platform, especially when not an IDE: some GUI-based Git client
Maven build and dependency management tool for the Java ecosystem
Mac and Linux users are strongly encouraged to use SDKMAN! to manage their Java, Maven, VisualVM, and other command-line development tools.
9.2.4. Choices of local development environments
Visual Studio Code (recommended for PlusCal/TLA+ development, supports Java development)
IntelliJ IDEA CE integrated development environment (alternative for Java development)
has unofficial Alloy and TLA+ plugins
check specific prerequisites for your platform
for the following steps, make sure you have no projects open and are looking at the welcome window as in the attached screenshot
JDK configuration: IntelliJ IDEA > Configure > Project Defaults > Project Structure > Platform Settings > SDKs > + > JDK > navigate to the installation directory of your Java 21 JDK > OK
conventional text editor (OK for general development but not recommended for working with Alloy or PlusCal/TLA+, though one can use them with the standalone TLA Toolbox)
Emacs
vim
etc.
9.3. Recommended Visual Studio Code extensions and settings
For consistency across VS Code installations, including Codespaces, enable settings sync using your GitHub or Microsoft/LUC account.
Install via the extensions tool in the VS Code toolbar:
Live Preview
Live Share
Extension Pack for Java
Alloy
Alloy VSCode
TLA+
Conceal, recommended for nicer rendering of mathematical symbols in TLA+ (see here and here for instructions)
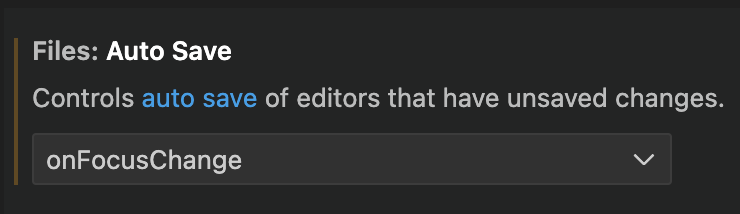
When running VS Code locally, autosave isn’t on by default, and you need to save your files manually: When there is a solid circle on the file’s tab, it’s not saved yet. I strongly recommend turning on autosave so your local instance of VS Code works the same way as browser-based instances:
click the cogwheel in the bottom left corner to open settings
type “autosave” in the search box
look for the actual setting and choose onFocusChange
9.4. GitHub
GitHub is a provider of hosted Git repositories, which emphasizes community and collaboration. For this reason, we use it to host our course examples.
Create a GitHub account if you don’t already have one.
Get the GitHub Student Developer Pack using your official
@luc.eduaddress. This will give you free unlimited private repositories.Find and follow a few practitioners you respect. For example, I follow these developers. You’ll probably recognize a number of them.
Review these notes to understand the community-based development process.
For credit toward class participation, create some meaningful GitHub issues and/or GitHub pull requests for one or more of our course examples. (Make sure to navigate to the original repos as these forks do not have their own issue trackers). These can be functional or nonfunctional enhancements, requests for clarification, etc.
To enhance your visibility in the professional community, start doing the same for some open-source projects you are interested in.
You may find both of these cheat sheets useful:
9.5. Remote participation
This software allows you to participating in class remotely in case of weather emergencies, pandemics, etc. For security and privacy reasons, be sure to update it frequently.
In case of a Zoom outage, we will fall back to MS Teams chat and reorganize from there.